Amanda Brown
Active member
Sony Semiconductor Solutions Company (SSS) has recently announced a groundbreaking development – a compact module that can transform electromagnetic noise into a power source for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize the way we power and operate these devices, even when not actively utilizing an electromagnetic radiation source. While the technology is currently in the developmental stage, its wide-ranging applications hold great promise for the future of IoT.
Measuring a mere 7x7 millimeters with a thickness of 1.2 millimeters, this compact module is designed to continuously power IoT devices. What sets it apart is its ability to harvest energy from electromagnetic noise present in our surroundings. This noise emanates from everyday household and industrial appliances such as lighting fixtures, automobiles, and even elevators.

Sony's module functions by utilizing the metallic components of IoT devices as antennas to capture electromagnetic waves within the frequency range of a few hertz to 100 megahertz. These captured waves are then transformed into electrical current through a specialized rectifier circuit, effectively providing a power source for IoT devices.
It's important to note that this technology is still in the development phase. However, the implications are significant. By creating a self-sustaining power source from ambient electromagnetic noise, Sony is poised to address a critical challenge in IoT – the need for long-lasting, autonomous power supplies.
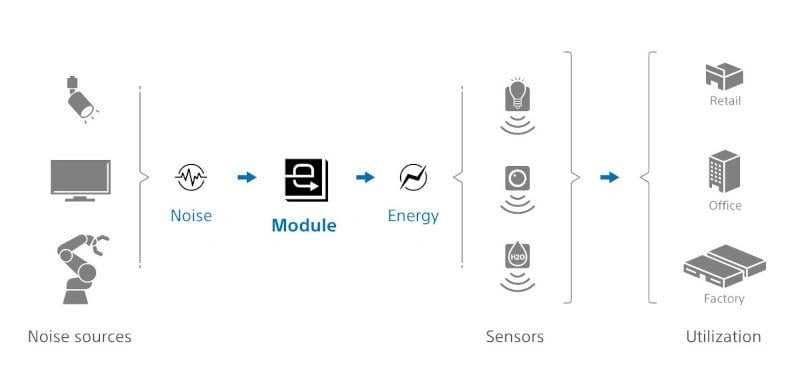
The potential applications for this technology are vast. IoT devices are becoming increasingly ubiquitous in our daily lives, from smart homes to industrial automation. Sony's innovative module has the potential to reduce the environmental footprint of these devices by eliminating the need for traditional power sources, such as batteries. This, in turn, could lead to more sustainable and efficient IoT solutions.
Sony's pioneering work in developing a module that converts electromagnetic noise into a viable power source for IoT devices represents a significant step forward in the world of connected technology. While it may take some time for this technology to reach commercialization, its promise in terms of sustainability and energy efficiency holds great potential for shaping the future of IoT.
Measuring a mere 7x7 millimeters with a thickness of 1.2 millimeters, this compact module is designed to continuously power IoT devices. What sets it apart is its ability to harvest energy from electromagnetic noise present in our surroundings. This noise emanates from everyday household and industrial appliances such as lighting fixtures, automobiles, and even elevators.

Sony's module functions by utilizing the metallic components of IoT devices as antennas to capture electromagnetic waves within the frequency range of a few hertz to 100 megahertz. These captured waves are then transformed into electrical current through a specialized rectifier circuit, effectively providing a power source for IoT devices.
It's important to note that this technology is still in the development phase. However, the implications are significant. By creating a self-sustaining power source from ambient electromagnetic noise, Sony is poised to address a critical challenge in IoT – the need for long-lasting, autonomous power supplies.

The potential applications for this technology are vast. IoT devices are becoming increasingly ubiquitous in our daily lives, from smart homes to industrial automation. Sony's innovative module has the potential to reduce the environmental footprint of these devices by eliminating the need for traditional power sources, such as batteries. This, in turn, could lead to more sustainable and efficient IoT solutions.
Sony's pioneering work in developing a module that converts electromagnetic noise into a viable power source for IoT devices represents a significant step forward in the world of connected technology. While it may take some time for this technology to reach commercialization, its promise in terms of sustainability and energy efficiency holds great potential for shaping the future of IoT.


