Catalogs Hide

Nowadays, we often get a variety of information by watching videos on TV or computer. For video data, the primary purpose of video coding is to compress the data in the video. VVC (also H.266) is one of the successors of standards-based codecs. This article will introduce you to what H.266 coding is.
What is H.266 coding?
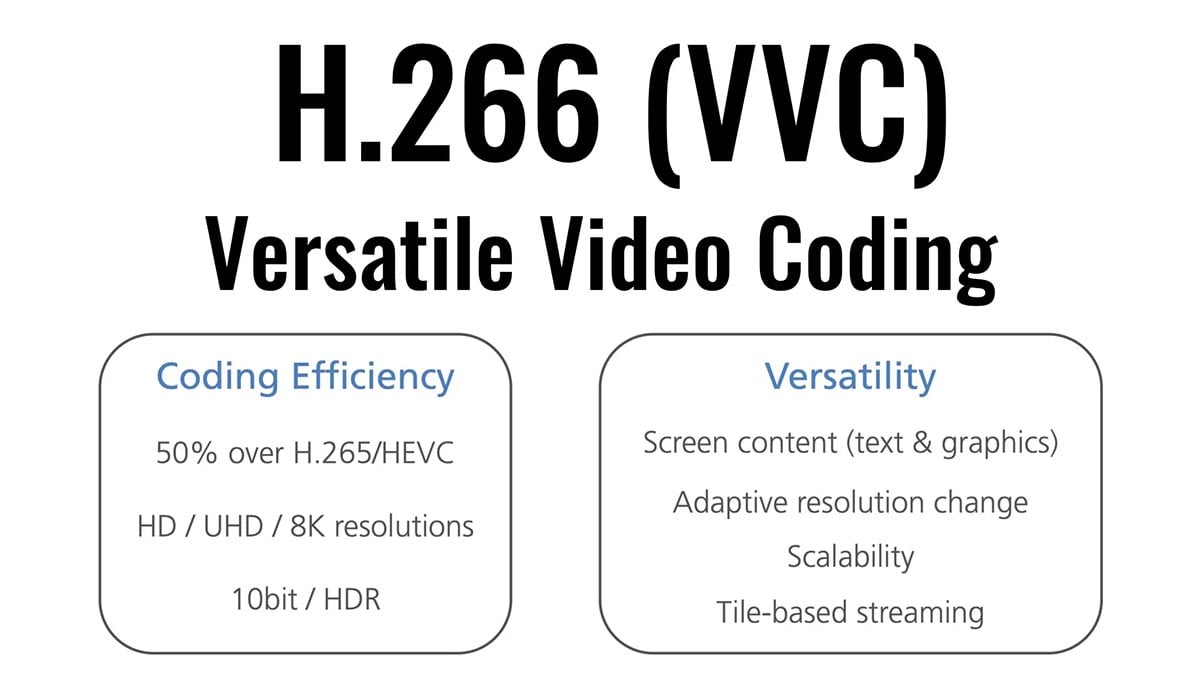
The H.266/VVC codec is a multi-functional video codec, and the mainstream video codecs on the market are H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, etc. H.266/VVC is the new generation of video coding standards after H.265, which was officially released in 2020, the latest generation of coding standards was officially released in November of that year.
The meaning VVC is an abbreviation for Versatile Video Coding, signifying that H.266 supports a wider range of applications.
H.266 is jointly developed by MPEG and ITU, and companies worldwide including Qualcomm, HHI, Huawei, Samsung, Sony, Intel, Nokia, Ericsson, Huawei, Tencent, and Ali are involved in it.
The H.266 codec can increase the efficiency of data compression and reduce the amount of data while maintaining the same clarity. The main features of H.266 are 4K and 8K services. Compared with the current mainstream H.264 and H.265, H.266 has better support for ultra-high definition, screen, high dynamic, 360° panoramic video, and other video types, as well as adaptive bandwidth and resolution streaming media.
What is video coding? Why do you need video coding?
We all know that video is composed of a large number of continuously played pictures. The principle is probably just like the earliest flip book, which uses long continuous motion pictures and uses human visual residue to make the pictures move.
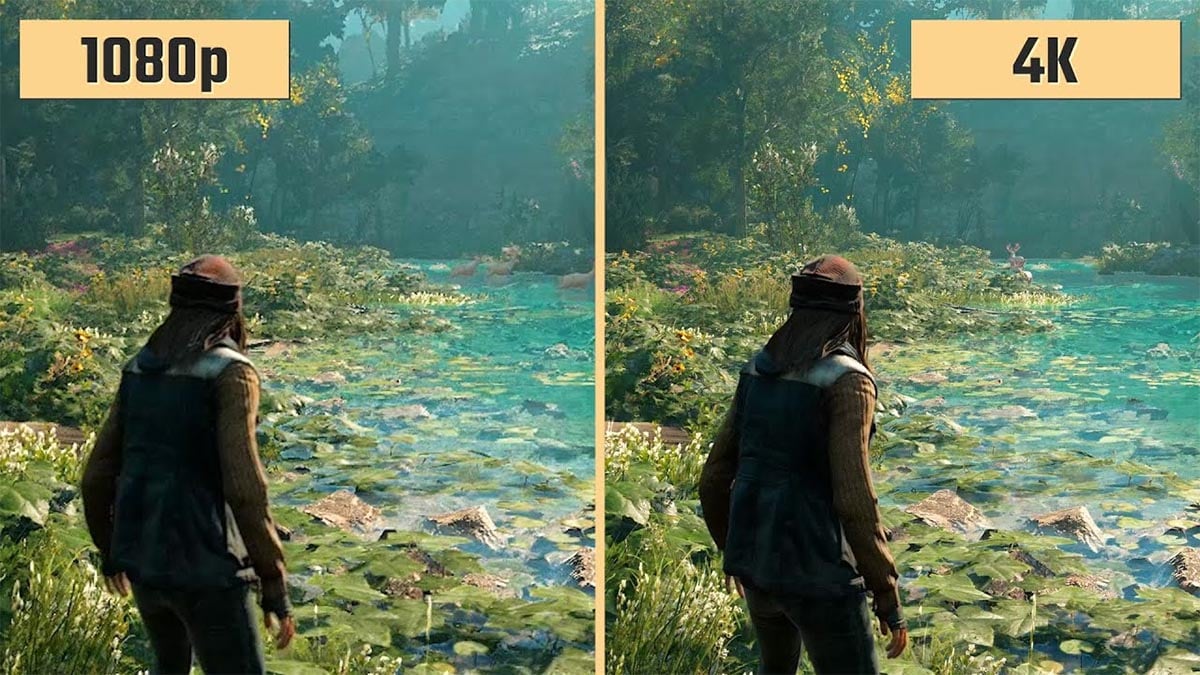

If we play 1080P 60 frames of video, then 1 second contains 60 similar images. Assuming the original image size is 5M, 1 second is 300M (5Mx60), and 1 minute of video is 18G (300Mx60). For this amount of video content, neither phones nor computers can handle it, so video coding is needed.
Therefore, video encoding means converting the original video format file into another video format file through compression technology. The daily videos we see are also compressed by the computer, and the size of the videos is not so exaggerated. Most of them are acceptable.
H.266 encoding optimizes the compression performance, that is to say, under the condition of constant clarity, resolution, and picture quality, if downloading a movie based on H.265 codec requires 4GB, then the traffic consumption based on H.266 codec technology only needs 2GB.
Will H.266 coding become mainstream in the future?
H.266/VVC compressed video in a similar way to H.265/HEVC, but with improvements in partitioning, prediction, and entropy coding (encoding without losing any information according to the entropy principle during encoding).
At present, H.266 has not reached the degree of popularity. If it is popularized, the industry related to HD video will usher in great changes. The main reason why H.266 is not popular is the cost problem. H.266 is not a free and open-source decoder, and there are patent problems unsolved at present. The high patent licensing cost makes many hardware manufacturers unable to bear it. H.265, which was released 10 years ago, has not been widely used due to high patent fees.
Characteristics of H.266
1. Lossless and subjective lossless compression
2.4K to 16K resolution and panoramic video
3.10 to 16-bit YCbCr 4:4:4, 4:2:2 and 4:2:0, BT.2100 wide gamut
4. High Dynamic Range (HDR) with a peak brightness of 1000, 4000, and 10000 Nits
5. Auxiliary channels (for recording depth, transparency, etc.)
6. Variable and fractional frame rates from 0 to 120 Hz
7. Adaptive video coding with respect to temporal (frame rate), spatial (resolution), signal-to-noise ratio, gamut, and dynamic range differences
8. Stereo/multi-view coding
9. Panoramic format
10. Still image coding
Summary
The core of the H.26x standard in video compression is the key to whether users can watch the high-definition video over the Web. Because HD video is too big to be watched on regular home broadband without compression, the stronger the encoding, the smaller the video, and the more HD video we can watch.



